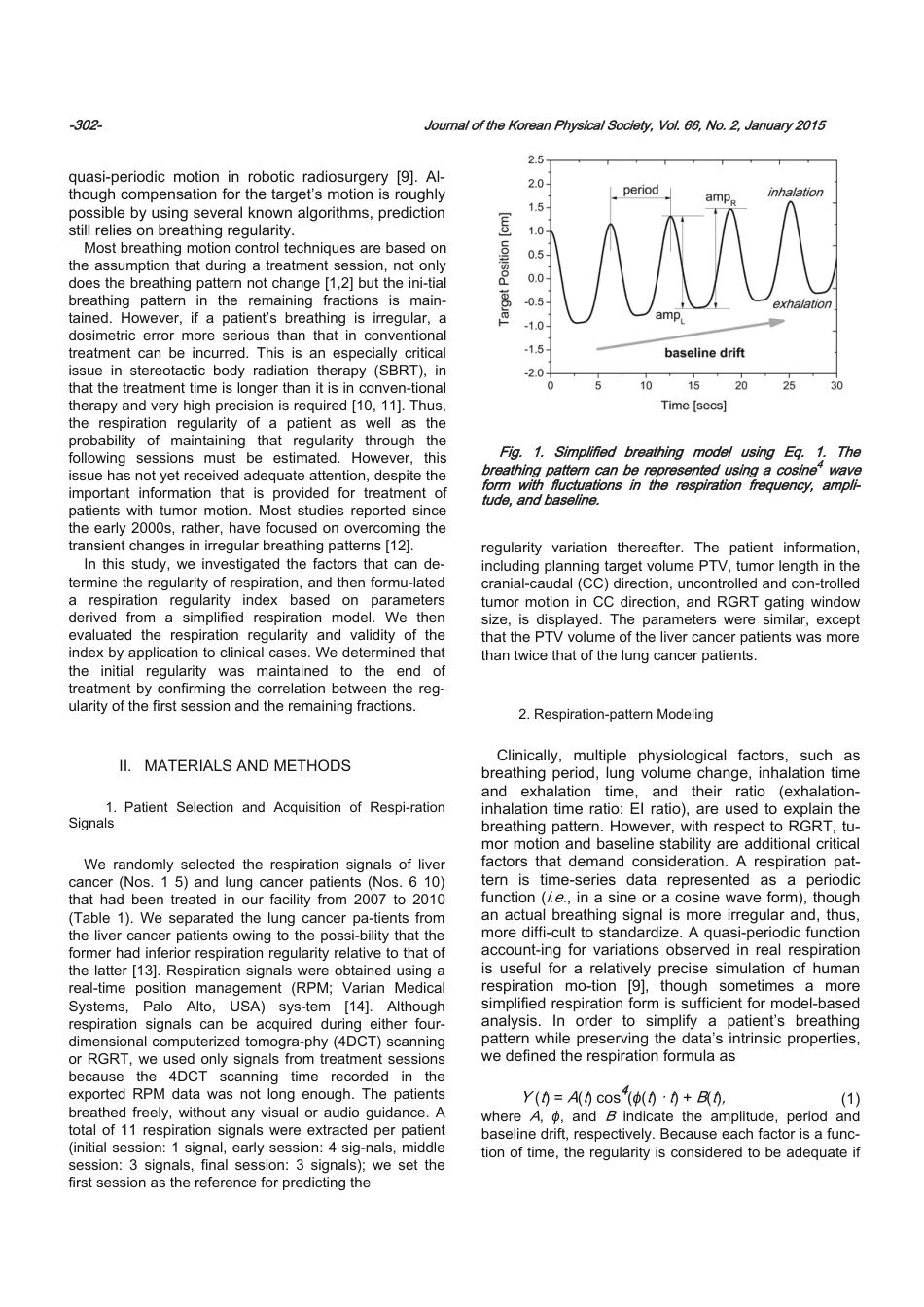
JournaloftheKoreanPhysicalSociety,Vol.66,No.2,January2015,pp.301313EvaluationofBreathingPatternsforRespiratory-gatedRadiationTherapyUsingtheRespirationRegularityIndexKwang-HoCheong,MeYeonLee,Sei-KwonKang,Jai-WoongYoon,SoAhPark,TaejinHwang,HaeyoungKim,KyoungJuKim,TaeJinHanandHoonsikBaeDepartmentofRadiationOncology,HallymUniversityCollegeofMedicine,Anyang431-070,Korea(Received3November2014)Despitetheconsiderableimportanceofaccuratelyestimatingtherespirationregularityofapatientinmotioncompensationtreatment,nottomentionthenecessityofmaintainingthatregularitythroughthefollowingsessions,aneectiveandsimplyapplicablemethodbywhichthosegoalscanbeaccomplishedhasrarelybeenffreported.Theauthorshereinproposeasimplerespirationregularityindexbasedonparametersderivedfromacorrespondinglysimplifiedrespirationmodel.Inordertosimplifyapatient’sbreathingpatternwhilepreservingthedata’sintrinsicproperties,wedefinedarespirationmodelasacos4(ω(t)·t)waveformwithabaselinedrift.Accordingtothisrespirationformula,breathing-patternfluctuationcouldbeexplainedusingfourfactors:thesamplestandarddeviationofrespirationperiod(sf),thesamplestandarddeviationofamplitude(sa)andtheresultsofasimpleregressionofthebaselinedrift(slopeasβ,andstandarddeviationofresidualsasσr)ω,whereωisavariableofarespirationsignal.Theoverallirregularity(δ)wasdefinedas||→−||→−newly-derivedbyusingprincipalcomponentanalysis(PCA)forthefourfluctuationparametersandhastwoprincipalcomponents(ω1,ω2).Theproposedrespirationregularityindexwasdefinedasρ=ln(1+(1/δ))/2,ahigherρindicatingamoreregularbreathingpattern.Weinvestigateditsclinicalrelevancebycomparingitwithotherknownparameters.Subsequently,weapplieditto110respirationsignalsacquiredfromfiveliverandfivelungcancerpatientsbyusingreal-timepositionmanagement(RPM;VarianMedicalSystems,PaloAlto,CA).CorrelationsbetweentheregularityofthefirstsessionandtheremainingfractionswereinvestigatedusingPearson’scor-relationcoefficient.Additionally,therespirationregularitywascomparedbetweentheliverandlungcancerpatientgroups.Therespirationregularitywasdeterminedbasedonρ;patientswithρ<0.3showedworseregularitythantheotherswhereasρ>0.7wassuitableforrespiratory-gatedradiationtherapy(RGRT).Fluctuationsinthebreathingcycleandtheamplitudewereespeciallydeterminativeofρ.Iftherespirationregularityofapatient’sfirstsessionwasknown,itcouldbeestimatedthroughsubsequentsessions.Notably,thebreathingpatternsofthelungcancerpatientsweremoreirregularthanthoseofthelivercancerpatients.Respirationregularitycouldbeobjec-tivelydeterminedbyusingacompositeindex,ρ.Suchasingle-indextestingofrespirationregularitycanfacilitatedeterminationofRGRTavailabilityinclinicalsettings,especiallyforfree-breathingcases.PACSnumbers:87.19.St,87.52.-g,87.53.Vb,87.56.-vKeywords:Breathingpattern,Respirationregularityindex,RPMsystem,Lung,LiverDOI:10.3938/jkps.66.301I.INTRODUCTIONInradiationtherapy,deliveryofanappropriatedosetotargetsinthelungortheupper-abdominalregionsiscomplicatedbyrespiratorymotion[1,2].Inoneinhale-exhalecycleforexample,alungtumorcanmoveasmuchas30mm[2].Imagingandbeam-deliverytech-niqueshavebeendevelopedtominimizetheeectsofffor-ganmotion,amongwhichmodalities,respiratory-gatedradiationtherapy(RGRT)andmotiontrackingtech-E-mail:b8510@hallym.or.kr;Fax:+82-31-380-3913niqueshavebecomepopularintheradiationoncologyfield[3–5].InRGR...