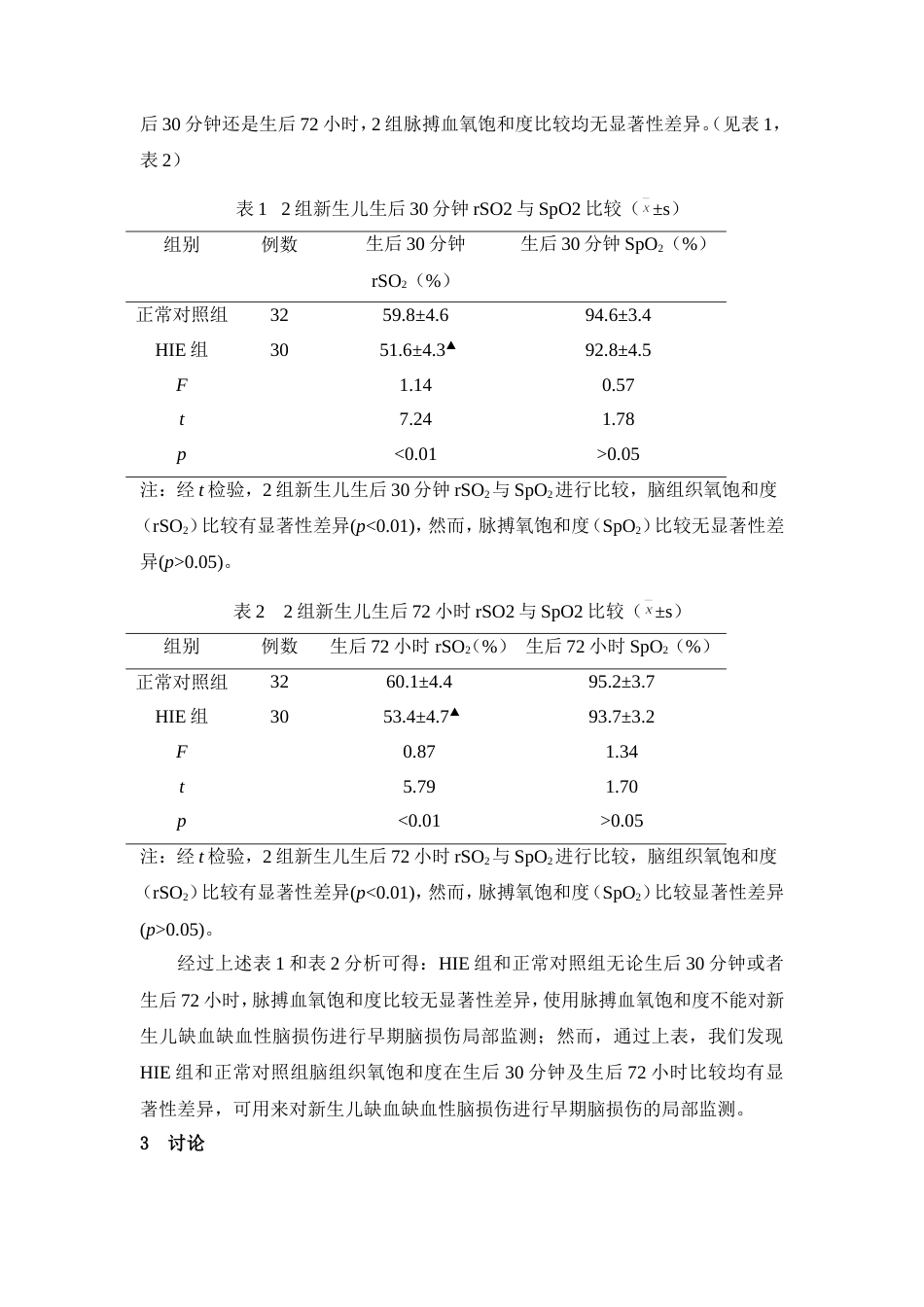
近红外光谱技术对新生儿缺氧性脑损伤的评价探讨谢小强,蒋丽红,苏国云深圳市光明新区公明人民医院新生儿科【摘要】目的:探讨近红外光谱技术对新生儿缺氧缺血性脑损伤和脑组织灌注的评价,为临床评价脑损伤提供客观依据。方法:应用近红外光谱技术和脉搏血氧饱和度监测技术,分别测定脑损伤患儿生后30分钟及生后72小时脑组织血氧饱和度与脉搏血氧饱和度,并与同时间点测定的正常对照组进行比较,以了解脑组织血氧饱和度测定与脉搏血氧饱和度测定在新生儿缺氧缺血性脑损伤早期评价方面的应用。结果:生后30分钟的缺氧缺血性脑病(hypoxicischemicencephalopathy,HIE)新生儿脑组织氧饱和度为51.6%±4.3%,低于正常对照组的59.8%±4.6%,差异有显著性(P<0.01),生后72小时HIE组新生儿脑组织氧饱和度为53.4%±4.7%,低于正常对照组的60.1%±4.4%,两者之间比较差异有显著性(P<0.01)。结论:在新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病时,脑组织氧饱和度测定比脉搏血氧饱和度测定更能客观的评价脑组织的损伤。【关键词】近红外光谱;脑组织氧饱和度;新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病Theevaluationofnear-infraredspectroscopyusedinneonatalhypoxicbraininjuryXieXiaoqiang,JiangLihong,SuGuoyunDepartmentofNeonatology,GongmingPeople'sHospital,GuangmingDistrict,Shenzhen【Abstract】Objective:Toexplorethenear-infraredspectroscopyonneonatalhypoxic-ischemicbraininjuryandbraintissueperfusionevaluationandtoprovideobjectivebasisforclinicalevaluationofbraininjury.Methods:usingnear-infraredspectroscopyandpulseoxygensaturationmonitoringtechnology,braintissueoxygensaturationandpulseoxygensaturationwasmeasuredonchildrenwithbraininjuryat30minutesafterbirth,and72hoursafterbirth,comparedwiththesamemeasurementonthenormalcontrolgroup,thebraintissueoxygensaturationandpulseoxygensaturationwasmeasuredfortheearlyevaluationofapplicationsinneonatalhypoxic-ischemicbraininjury.Results:30minutesafterbirth,hypoxic-ischemicencephalopathy(HIE)neonatalbraintissueoxygensaturation(51.6%±4.3%),lowerthanthecontrolgroup(59.8%±4.6%),thedifferencewassignificant(p<0.01),while72hoursafterbirth,HIEbraintissueoxygensaturation(53.4%±4.7%),lowerthanthecontrolgroup(60.1%±4.4%),thedifferencebetweenthetwosignificant(p<0.01).Conclusion:Inneonateswithhypoxicischemicencephalopathy,braintissueoxygensaturationhasmoreobjectiveassessmentthanpulseoxygensaturationinthedeterminationofbraintissuedamage.【Keywords】:Near-infraredspectroscopy;braintissueoxygensaturation;neonatalhypoxic-ischemicencephalopathy新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病(hypoxicischemicencephalopathy,HIE)在围产期神经系统疾病中占有重要位置,是由于各种围生期因素引起的部分或完全性缺氧和脑血流量减少或暂停而导致胎儿和新生儿的脑损伤[1-2]。据统计,我国每年活产婴1800万-2000万,窒息的发病率为13.6%,在窒息患儿中,发生不同程度伤残者为15.6%,故新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病多年来受到国内外学者的广泛关注[1]。目前,脑组织氧饱和度(regionaloxygensaturation,rSO2)已能得出量化的数值。本实验通过探讨近红外光谱(nearinfraredspectroscopy,NIRS)技术对缺氧缺血性脑损伤评判的价值,为临床评价新生儿缺氧缺血性脑损伤提供客观、量化依据。1对象与方法1.1研究对象患病组30例,为2006年6月~2008年10月于我院产科分娩的正常妊娠,胎位正常,分娩过程中有明确胎儿宫内窘迫的患儿(孕母有心肾疾病、贫血、感染性疾病者不列入,早产儿除外),其中男19例,女11例,胎龄37~43周,平均(38.9±2.4)周,出生体重2762~4240g,平均(3453±406)g。此列患儿符合由中华医学会儿科分会新生儿组指定的足月儿HIE诊断标准如下:①有明确的可导致胎儿宫内窘迫的异常产科病史,以及严重的胎儿宫内窘迫表现(胎心率<100次/分,持续5分钟以上和(或)羊水Ⅲ度污染),或在分娩过程中有明显窒息史;...