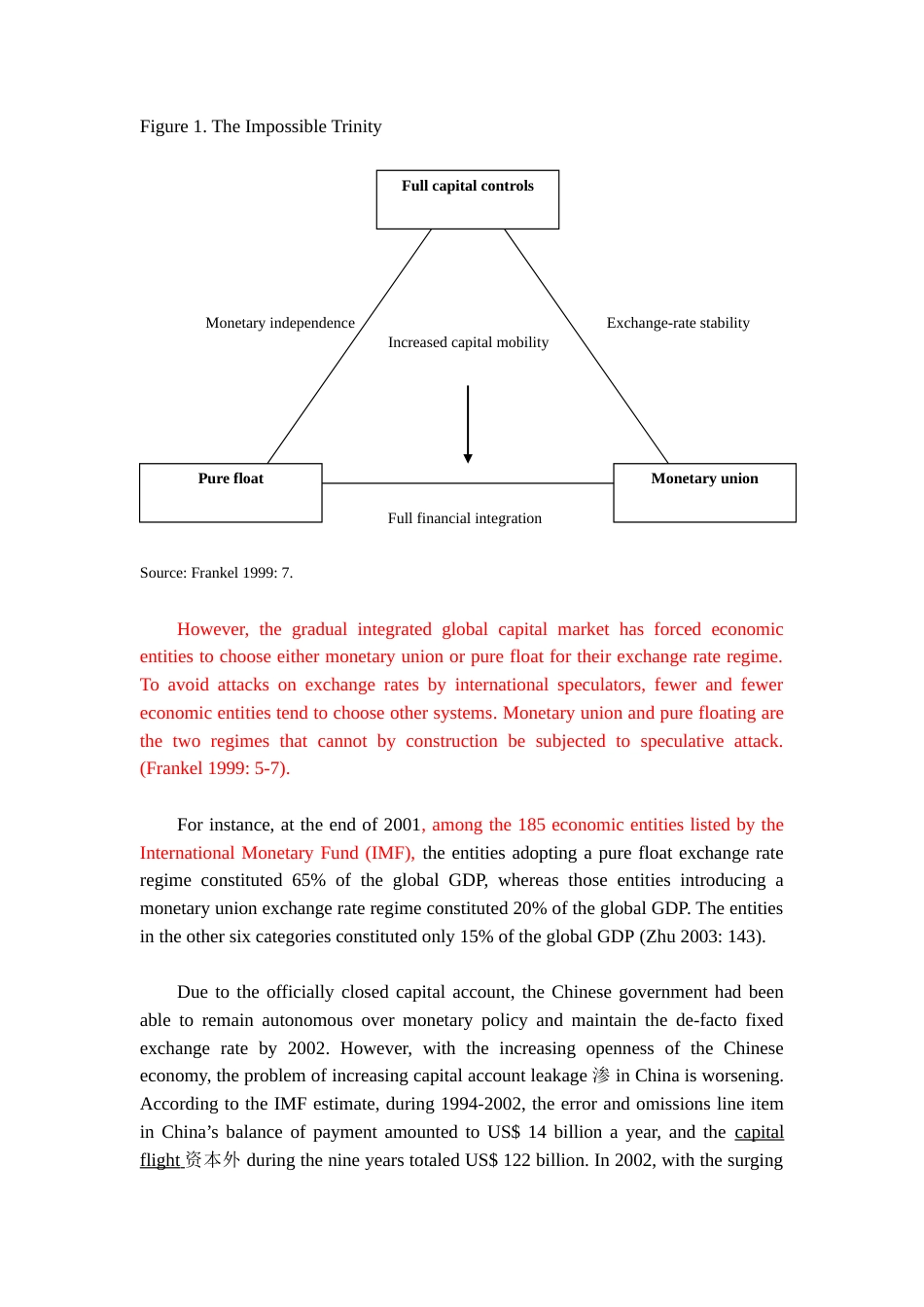
TheRenminbiExchangeRateintheIncreasinglyOpenEconomyofChina:AShort-RunSolutionandALong-RunStrategyCHEN-YUANTUNGAssistantResearchFellowInstituteofInternationalRelationsNationalChengchiUniversityE-mail:ctung@jhu.eduTel:886-2-8237-7356Abstract:ApracticalapproachfortheChinesegovernmenttosolvethecurrentcurrencydilemmaistoallowtheRMBtoappreciateby10-15%immediatelyandchangetheRMBexchangerateregimefromthede-facto事实上fixedUSdollarpegtoanewmechanismlinkingtheRMBtoabasketofcurrencies,whileexpandingthefloatingbandoftheRMBexchangeratefrom1%to5-7%.Nevertheless,thereisnotimetablefortheadjustmentoftheexchangerateofRMBaslongastheChinesegovernmentcantoleratetheeconomicoverheatingandimbalanceresultedfromtheundervaluedexchangerate.But,aslongasChina’seconomyremainsoverheatedandtheexpectationofanRMBrevaluationpersists,internationalhotmoneymaycontinuetoflowintoChinaandwouldprobablycause“self-fulfillingprophecy”自我实现的预言appreciationoftheRMB.JELclassification:F31,F41.Keywords:Renminbiexchangerate;exchangerateregime;impossibletrinity三元悖论;balance-of-paymentcrisesmodels;hotmoney.*PaperpresentedattheWesternEconomicAssociationInternational6thPacificRimConference,LingnanUniversity,HongKong,January15-16,2005.I.IntroductionOnJanuary1,1994,ChinaadoptedanewmanagedfloatregimewiththeRenminbi(RMB)exchangerateat8.7perUSdollar(USD)withanarrowbandof0.25%ofthepreviousday’sreferencerate参考汇率.Underthenewregime,theRMB/USDexchangeratebegantoappreciateto8.3inMay1995and8.28inOctober1997.DuringtheAsianfinancialcrisis,thetradingbandwasnarrowedfurtherandtheexchangerateofRMB8.28perdollarhasbeenmaintainedtothepresent(January2005).Thus,althoughtheofficially-claimedexchangerateregimeisstillamanagedfloatregime,Chinahasessentiallyoperateditssystemasade-factofixedpegtothedollarsince1994.AstablecurrencyregimehasservedChinawell,beingroutinelycitedbyChinesepolicymakersandforeignpundits学者alikeasanimportantfactorinfacilitatingChina’sgrowthmiracleoverthepastdecade,particularlyattractingforeigndirectinvestment(FDI)andfacilitatetrade.InthewakeoftheAsianfinancialcrisisof1997-98,China’scommitmenttoafaxedexchangeratetothedollarwaswidelypraisedasakeyanchorfortheglobalfinancialsystem.However,thegenerallysupportiveglobalconsensusregardingChina’sstableexchange-rateregimehasevaporatedoverthepastthreeyears.FromearlyJanuaryof2002toearlyJanuaryof2004,theUSdollardepreciatedagainsttheEurobyaround40%,againsttheJapaneseYenby25%,againsttheTaiwandollar,theSingaporeandollar,andtheKoreanWonby5-12%.In2004,theUSdollarcontinuestodepreciateagainstthesecurrenciesby4.1-15.6%andthetrendisexpectedtocontinue.UnderChina’sde-factofixedexchangerateregime,theRMBhasdepreciatedagainsttheabovecurrenciesbythesamemarginsinnominalterms.Fromthebeginningof2002totheendofsummer2004,thetrade-weightedexchangerateoftheRMBdepreciatedby8%,whichiscontributingtotheimbalancedRMBexchangeratesystem.(GoldsteinandLardy2004)Thenominaldepreciation名义oftheRMBhasresultedinwidespreadcomplainsthatChinaisunfairlymanipulating操纵itscurrencytogainacompetitivetradeadvantage.Nevertheless,theChinesegovernmenthasfirmlyinsistedonthede-factofixedRMB/USDexchangerateinordertoprotectexportcompetitivenessandavoidfurtherunemploymentpressure.(GovernorZhouXiaochuan2003)TheChinesegovernmentarguedthatthestableRMBexchangerateisinbothChina’sandglobalinterest.(Hung2004)Attheheartofthedebat...