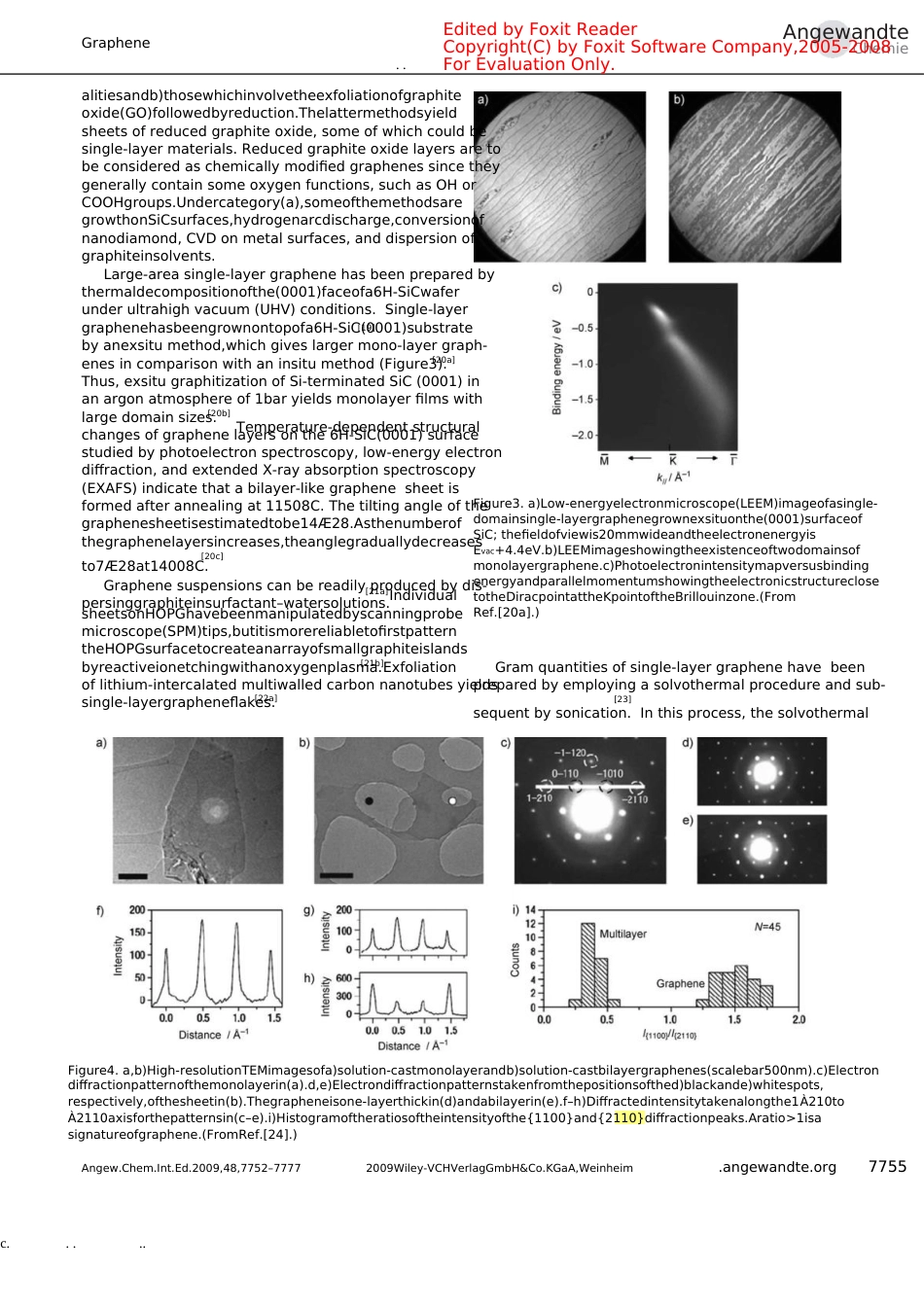
.....c.....ReviewsC.N.R.Raoetal.DOI:10.1002/anie.200901678NanomaterialsGraphene:TheNewTwo-DimensionalNanomaterialC.N.R.Rao,*A.K.Sood,K.S.Subrahmanyam,andA.GovindarajKeywords:carbon·graphene·grapheneoxide·monolayers·nanostructuresAngewandteChemie7752.angewandte.org2009Wiley-VCHVerlagGmbH&Co.KGaA,WeinheimAngew.Chem.Int.Ed.2009,48,7752–7777.....c.....EditedbyFoxitReaderAngewandteChemieGrapheneCopyright(C)byFoxitSoftwareCompany,2005-2008ForEvaluationOnly.Everyfewyears,anewmaterialwithuniquepropertiesemergesandFromtheContentsfascinatesthescientificcommunity,typicalrecentexamplesbeinghigh-temperaturesuperconductorsandcarbonnanotubes.Grapheneisthelatestsensationwithunusualproperties,suchashalf-integerquantumHalleffectandballisticelectrontransport.Thistwo-dimen-sionalmaterialwhichistheparentofallgraphiticcarbonformsisstrictlyexpectedtocompriseasinglelayer,butthereisconsiderableinterestininvestigatingtwo-layerandfew-layergraphenesaswell.Synthesisandcharacterizationofgraphenesposechallenges,buttherehasbeenconsiderableprogressinthelastyearorso.Herein,wepresentthestatusofgrapheneresearchwhichincludesaspectsrelatedtosynthesis,characterization,structure,andproperties.1.Introduction7753775477602.Synthesis3.ElectronicStructure4.PhononsandRamanSpectroscopy776277645.EffectsofDoping6.FunctionalizationandSolubilization77677.DecorationwithMetalandMetalOxideNanoparticles77697770777377731.Introduction8.PropertiesGraphene,theparentofallgraphiticforms(Figure1),hasbecomeoneofthemostexcitingtopicsofresearchinthelastthreetofouryears.9.PolymerComposites10.Outlook[1]Thistwo-dimensionalmaterialconsti-tutesanewnanocarboncomprisinglayersofcarbonatomsarrangedinsix-memberedrings.Itisdistinctlydifferentfromcarbonnanotubes(CNTs)andfullerenes,andexhibitsuniquepropertieswhichhavefascinatedthescientificcommunity.TypicallyimportantpropertiesofgrapheneareaquantumHalleffectatroomtemperature,fieldeffectalongwithballisticconductionofchargecarriers,tunablebandgap,andhighelasticity.Althoughgrapheneisexpectedtobeperfectlyflat,ripplesoccurbecauseofthermalfluctuations.Ideallygrapheneisasingle-layerseveralstrategieshavesincebeendevelopedforthesynthesisofgraphenes.Graphenehasbeencharacterizedbyavarietyofmicro-scopicandotherphysicaltechniquesincludingatomicforce[2–4]anambipolarelectric[8][5][6][7]microscopy(AFM),transmissionelectronmicroscopy[1](TEM),scanningtunnelingmicroscopy(STM),X-raydif-material,butgraphenesampleswithtwoormorelayersarefraction(XRD),andRamanspectroscopy.Itisinterestingbeinginvestigatedwithequalinterest.Threedifferenttypesofgraphenescanbedefined:single-layergraphene(SG),bilayergraphene(BG),andfew-layergraphene(FG,numberoflayersµ10).Althoughsingle-layergrapheneandbilayer[1]thatsingle-layergrapheneplacedonasiliconwaferwitha300nmthicklayerofSiO2,becomesvisibleinanopticalmicroscope(Figure2aandb).WhileAFMdirectlygivesthenumberoflayers(Figure2c),STM(Figure2d)and[11]TEM(Figure2e)imagesareusefulindeterminingthe[8–10][8]graphenewerefirstobtainedbymicro-mechanicalcleavage,[5][12]morphologyandstructureofgraphene.Ramanspectroscopyhasemergedtobeanimportanttoolforthecharacterizationofgraphenesamples.Herein,weshalldiscussvarious[13–16]aspectsofgraphene,includingsynthesis,structure,properties,functionalization,andpolymercomposites.AlthoughwehavecoveredmostoftheimportantfacetsofgraphenepublisheduptoMay2009,weh...