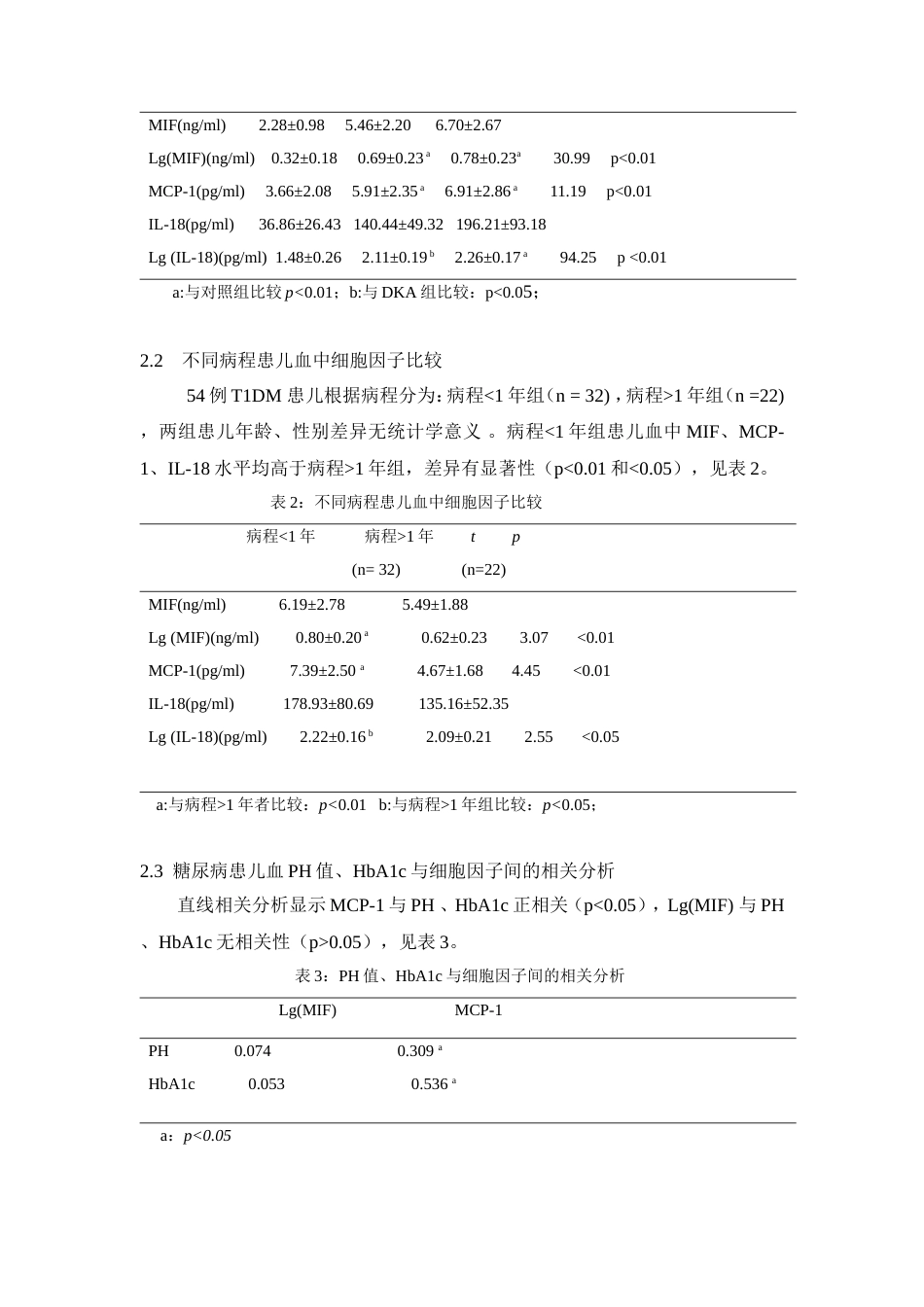
1型糖尿病儿童血MIF和MCP-1水平及临床意义杨卫霞徐美玉*黄锋张向东蔡晋申飞飞(南通大学附属医院儿内科,江苏南通226001)【摘要】目的:探讨1型糖尿病儿童血巨噬细胞移动抑制因子(Macrophagemigrationinhibitoryfactor,MIF)和单核细胞趋化蛋白-1(Monocytechemoattractantprotein-1,MCP-1)以及白介素-18(Interleukin-18,IL-18)水平及临床意义。方法:对2011年11月至2013年4月在该院就诊的54例1型糖尿病患儿进行MIF、MCP-1、IL-18、糖化血红蛋白、血pH值检测,根据患儿有无酮症酸中毒分为DKA组和非DKA组,另选25例正常体检健康儿童作为对照组。分析比较疾病不同严重程度、不同病程患儿血中MIF、MCP-1、IL-18水平的差异,同时寻找血pH值、HbA1c与相关细胞因子间的关系。结果:1、与健康对照组比较,MIF、MCP-1、IL-18水平在1型糖尿病患儿中显著升高(p<0.01),而IL-18在DKA组中的水平高于非DKA组,差异有显著性(p<0.05)。2、病程小于一年患儿MIF、MCP-1、IL-18水平高于病程大于一年患儿,差异有显著性(p<0.01和<0.05)。3、直线相关分析显示MCP-1与PH、HbA1c正相关(p<0.05),Lg(MIF)与PH、HbA1c无相关性(p>0.05)。结论:MIF,MCP-1、IL-18在1型糖尿病中的水平较正常儿高,新发病者尤其明显,该类细胞因子参与了儿童1型糖尿病的发生和发展,MCP-1可联合糖化血红蛋白评价患儿近期血糖水平。【关键词】1型糖尿病;巨噬细胞移动抑制因子;单核细胞趋化蛋白-11TheserumlevelandclinicalvalueofMIFandMCP-1intype1diabetesmellitusinchildrenYangWeixia,XuMeiyu*.HuangFeng,ZhangXiangdong,CaiJin,ShenFeifei(DepartmentofPediatrics,AffiliatedHospitalofNantongUniversity,Nantong,Jiangsu226001,China)【Abstract】Objective:TostudytheclinicalvalueofMIF,MCP-1,interleukin-18intype1diabetesmellitus(T1DM)inchildren.Methods:TheSerumcytokinesandantibodylevelsweremeasuredin54childrenwithtype1diabetesmellitusdiagnosedintheAffiliatedHospitalofNantongUniversityfromNovember2011toApril2013.Thediabeticchildrenwereclassifiedintotwosubgroupswithorwithout1*[通信作者]Email:xumeiyu_nt@hotmail.comketoacidosis,another25healthychildrenascontrolgroup.Differentcytokineslevelswerecomparedamongdifferentgroupsaccordingtodiseaseseverityandcourse,atthesametime,therelationshipbetweenHbA1c,pHandrelatedcytokineswereanalysised.Results:1,MIF,MCP-1,IL-18levelswassignificantlyhigherinchildrenwithtype1diabetesthanthatinhealthychildren(p<0.01),andIL-18washigherinketoacidosisthanthatwithoutDKA(p<0.05).2,MIF,MCP-1,IL-18levelsweresignificantlyhigherinchildrenwithrecent-onsettype1diabeteswithinoneyearthanthatoveroneyear,(p<0.01and<0.05).3LinearcorrelationanalysisshowedpositivecorrelationbetweenpH,HbA1candMCP-1(p<0.05),whileMIFwasnotcorrelatedwithpHandHbA1c(p>0.05).Conclusion:MIF,MCP-1,IL-18levelsintype1diabeteswerehigherthanthatinhealthychildren,especiallyfornewcases.MCP-1canbeevaluationofshort-termbloodglucoselevelscombinedwithglycosylatedhemoglobin.【Keywords】Type1diabetesmellitus;Macrophagemigrationinhibitoryfactor;Monocytechemoattractantprotein-1糖尿病是由多种病因引起的以慢性高血糖为特征的代谢紊乱性疾病。1型糖尿病(Type1diabetesmellitus,T1DM)是一种由T淋巴细胞介导的自身免疫性疾病,其特征表现为胰岛β细胞破坏,胰岛素生成与释放减少。细胞因子在其发病和病情进展中起重要作用。巨噬细胞移动抑制因子和单核细胞趋化蛋白-1是两种重要的细胞因子,国外研究发现该因子和2型糖尿病的发病及病情进展有重要的关系[1],但在儿童1型糖尿病中的研究较少。本研究分析比较疾病不同严重程度、不同病程1型糖尿病患儿血中MIF和MCP-1等细胞因子的差异,探讨该类细胞因子在儿童T1DM发病中的意义。1资料与方法1.1研究对象2011年11月至2013年4月南通大学附属医院就诊的1...