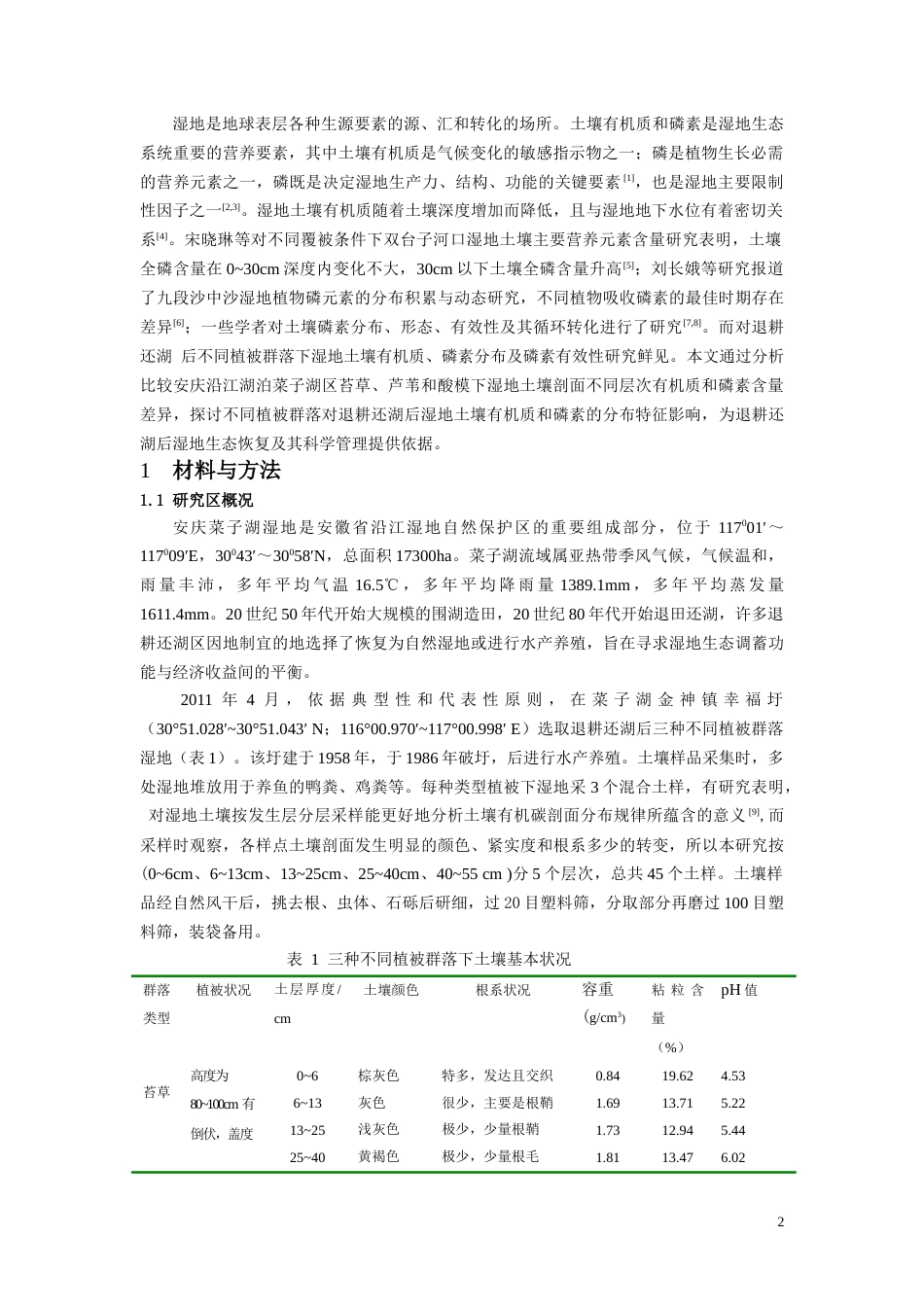
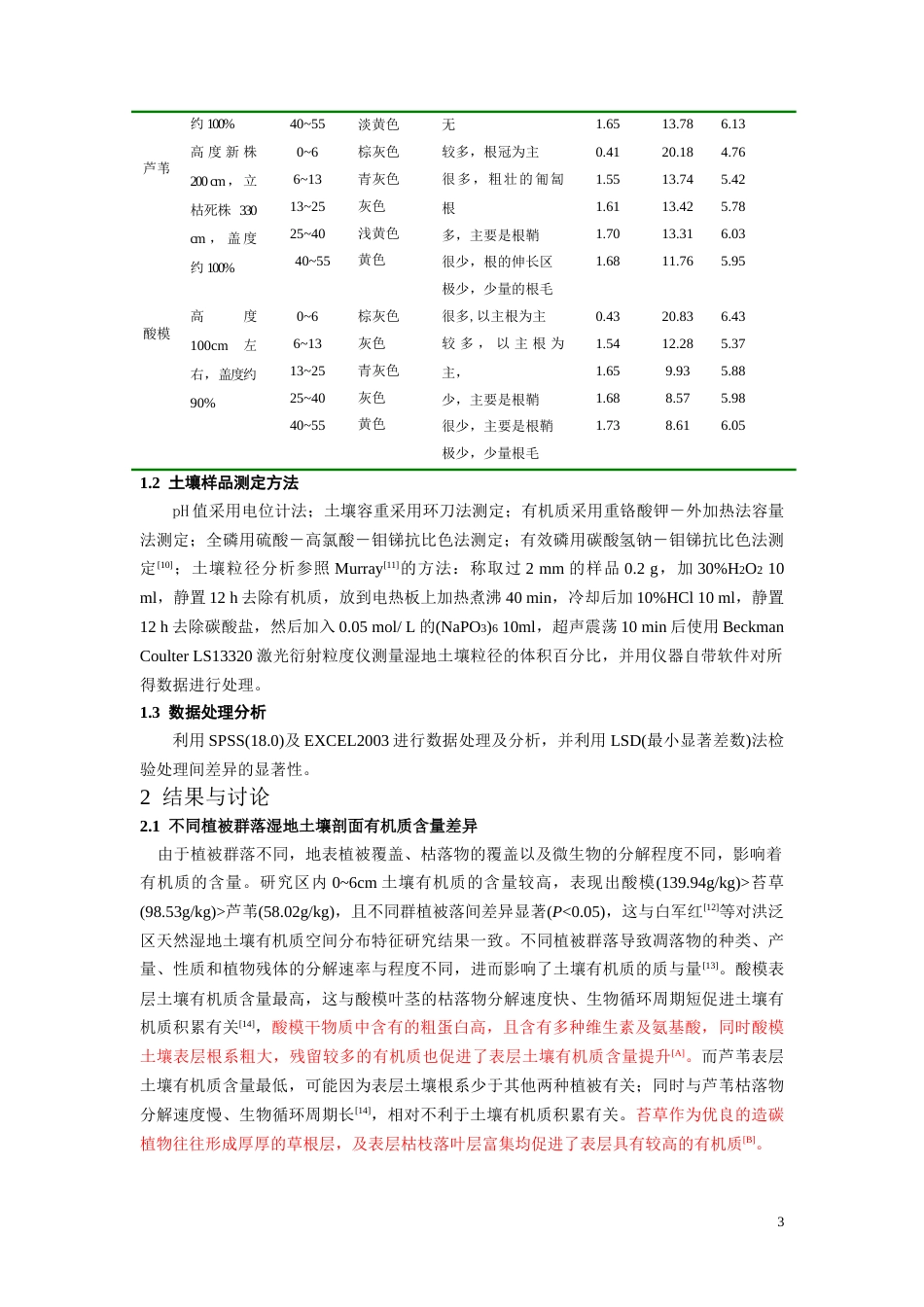
退耕还湖后不同植被群落下湿地土壤有机质及磷素含量差异崔宏,张平究,孔令柱,郑真,刘爽(安徽自然灾害过程与防控研究省级重点实验室/安徽师范大学国土资源与旅游学院,安徽芜湖241000)摘要:以菜子湖地区退耕还湖后苔草、芦苇和酸模植被群落下的湿地土壤为研究对象,分析三种植被群落类型对土壤有机质、全磷、速效磷含量及其在土壤剖面分布特征的影响。结果表明:0~6cm土壤有机质含量表现为酸模>苔草>芦苇,而6~13cm、13~25cm、25~40cm、40~55cm均表现为芦苇>苔草>酸模,总体均表现为随着土壤剖面深度增加而下降;土壤全磷含量均为0~6cm层含量较高,6~13cm层最低,随着剖面深度的增加而递增,递增趋势酸模最为明显,苔草次之,再为芦苇;除酸模0~6cm土壤速效磷的含量显著大于苔草和芦苇外,其他各个层次间土壤有效磷含量无显著性差异,但总体上均有在垂直方向上随剖面加深而下降的趋势;酸模0~6cm和6~13cm层次土壤磷素有效率显著高于苔草和芦苇外,其他不同土壤层次间无显著差异。分析表明不同植被群落凋落物和根系分布特征是引起土壤剖面有机质和磷素分布差异的原因。关键词:退耕还湖;植被群落;湿地土壤;有机质;磷素:S151.93;S158.3VariationofSoilOrganicMatterandPhosphorusContentsUnderDifferentVegetationTypesWetlandsunderReturningFarmlandtotheLakeCUIHong,ZHANGPing-激u,KONGLing-zhu,ZHENGZhen,LIUShuang(AnhuiKeyLaboratoryofNaturalDisastersProcessandPrevention/CollegeofTerritorialResourceandTourism,AnhuiNormalUniversity,Wuhu241003,China.)Abstract:SoilsfromwetlandsinCaiziLakeadoptingreturningfarmlandtolakeofcarex,reedandsorrelvegetationweresampledtoanalyzetheeffectofthreevegetationcommunitytypesofsoilorganicmatter,totalPandavailablePanditsdistributioninthesoilprofilefeatures.Theresultsshowthatthesoilorganicmattercontainedin0~6cmlayerisRumexacetosaLinn>sedge>Phragmitesaustralis,whileinalltheotherlayers(including6~13cm、13~25cm、25~40cm、40~55cm)therelationshipbetweenthethreevegetationcommunitiescanbeexpressedasPhragmitesaustralis>sedge>RumexacetosaLinn,whichbasicallysatisfythatthedeeperofthesoilprofilesoil,thelowerofallthethreetypesvegetationscontainedinthesoil.ForthetotalP,allthethreevegetationcommunitieshavethesameproperty,theycontainthehighesttotalPin0~6cmandlowestin6~13cm.Moreover,thedeeperofthesoilprofilesoil,thehigherofallthethreetypesvegetationscontainedinthesoilwithRumexacetosaLinn>sedge>Phragmitesaustralis.FortheavailableP,allthethreevegetationcommunitieshavealmostthesameamountinvariouslayerswhichobsesssimilarlypropertywithsoilsorganicmatter,exceptthatRumexacetosacontainedin0~6cmishigherthantheothertwo.Inconclusion,littersandrootdistributionunderdifferentvegetationtypesarethecauseofdistributionvariationoforganicmatterandphosphoruscontentinthesoilprofiles.Keywords:returningfarmlandtolake;vegetationcommunity;wetlandsoil;organicmatter;P基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(41001369);安徽省高校省级自然科学研究项目(KJ2008B264);安徽师范大学博士基金;安徽师范大学专项基金(2007xzx14).作者简介:崔宏(1983-),女,安徽灵璧人,硕士研究生,研究方向:湿地土壤环境.E-mail:cuihon060811@sohu*通讯作者:张平究(1975-),男,江西玉山人,博士,副教授.E-mail:changpj2006@yahoo.1湿地是地球表层各种生源要素的源、汇和转化的场所。土壤有机质和磷素是湿地生态系统重要的营养要素,其中土壤有机质是气候变化的敏感指示物之一;磷是植物生长必需的营养元素之一,磷既是决定湿地生产力、结构、功能的关键要素[1],也是湿地主要限制性因子之一[2,3]。湿地土壤有机质随着土壤深度增加而降低,且与湿地地下水位有着密切关系[4]。宋晓琳等对不同覆被条件下双台子河口湿地土壤主要营养元素含量研究表明,土壤全磷含量在0~30cm...